HYPOTHERMIA
DEFINITION
Hypothermia is a potentially dangerous condition that is defined as a core body temperature below 95ᵒF caused by prolonged exposure to cold temperatures. If left untreated it can cause serious damage like heart attack, Liver damage, kidney failure & Death.
CAUSES OF HYPOTHERMIA
- Decreased Heat production:
- Endocrine disorders:
- Deficiency in hormones like hypopituitarism, hypoaldosteronism & Hypothyroidism causes decreased metabolic activity & decreases body temperature
- Severe Malnutrition:
- Malnutrition decreases the basal metabolic rate of the body and decreases body temperature
- Hypoglycemia:
- In hypoglycemia there is decreased levels of glucose as compensatory mechanism the body tries to preserve energy which results in decreased body temperature
- Neuro Muscular Dysfunction:
- Hypothermia develops in neuromuscular dysfunction due to reduced heat production by Inactive muscles
- Increased Heat Loss:
- Skin Disorders (Erythroderma):
- A condition that occurs in burns & Psoriasis where there is decreased ability of the body to preserve heat that results in decreased body temperature
- Iatrogenic causes:
- Cold Infusions like cool fluids and blood products, over treatment for heat stroke, exposure to perioperative cold temperatures can cause hypothermia due to Increased heat loss
- Pharmacologic Agents:
- Pharmacologic agents like vasodilators, ethanol, sedatives, hypnotics anesthetic Agents, beta blockers, clonidine can reduce the body’s ability to respond to low temperatures and causes hypothermia
- Impaired Thermoregulation:
- CNS Disorders:
- CNS Trauma, Stroke, Intra cranial bleeding, Parkinson’s Disease, Multiple Sclerosis, Anorexia Nervosa, Hypothalamic dysfunction can cause metabolic derangements in the body resulting in impaired thermoregulation that decreases the body temperature
CLASSIFICATION OF HYPOTHERMIA
- Primary Hypothermia:
- This is due to exposure to cold environment with no underlying medical condition causing disruption of temperature regulation and susceptible to hypothermia
- Peri-Operative Hypothermia:
- Accidental Hypothermia: Patients whose core temperature drops below 36ᵒC during the peri-operative period i.e from the hour of Induction of Anesthesia until 24 hours after entering the recovery area
- Intentional hypothermia : It is an induced state generally directed at neuroprotection after an at-risk situation (usually after cardiac arrest)
- Secondary Hypothermia:
- This is low body temperature resulting from a medical illness that lowers the temperature set-point like endocrine Disorders, skin disorders, CNS disorders & Pharmacologic Agents.
- Therapeutic Hypothermia:
- Therapeutic hypothermia or protective hypothermia is an active treatment used for people with post cardiac arrest. Once the hearts starts to contract again health care providers use cooling devices to lower the body temperature for a short duration.
RISK FACTORS OF HYPOTHERMIA
- Very young and very elderly patients
- Patients who are chronically ill especially with cardiovascular diseases
- Malnourished people
- People who are very tired & Exhausted
- Patients with Alcohol & Drug Intoxication
- Clients with cognitive Impairment like in Alzheimer's Disease
- Clients with underlying medical Illness such as Stroke, Arthritis, Spinal cord Injuries, neurologic disorders & Burns.
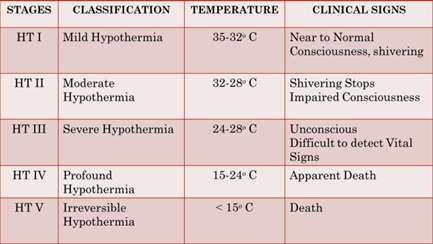
STAGING OF HYPOTHERMIA
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF HYPOTHERMIA

CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
- Shivering, which may stop as hypothermia progresses (shivering is actually a good sign that a person's heat regulation systems are still active. )
- Slow, shallow breathing
- Confusion and memory loss leading to coma
- Drowsiness or exhaustion
- Slurred or mumbled speech
- Loss of coordination, Impaired gait
- Cognitive Signs like Irritability, lassitude, poor Judgment
- Mood Changes
- Rhythmic or repeated movements like rocking
- A slow, weak pulse
- In severe hypothermia, a person may be unconscious without obvious signs of breathing or a pulse
DIAGNOSTIC FINDINGS OF HYPOTHERMIA
- Temperature Monitoring: To Identify & classify the types of Hypothermia
- ABG Analysis: Shows elevated levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in Hypothermia
- Hematocrit: Hematocrit levels may increase 2% for each 1°C drop in core temperature.
- Sr. Electrolytes: Chronic hypothermia can lead to hypokalemia
- Blood Glucose: Blood Glucose levels are Increased initially leading to sever hypoglycemia in case of chronic Hypothermia
- Coagulation Studies: Bleeding time, clotting time, Prothrombin time, thrombin time, partial Thromboplastin time are deranged in case of Hypothermia
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): To monitor heart function & QT intervals are prolonged in case of Hypothermia
- Imaging Studies:
- Chest X-ray: To rule out any heart or lung disorders
- CT Scan: To evaluate Neurologic disorders like trauma & Hemorrhage
MEDICAL MANAGEMENT OF HYPOTHERMIA
- Careful Handling:
- Handle the affected person with care. Don’t massage them in an attempt to restore blood flow. Any forceful or excessive movements may cause cardiac arrest. Move or shield the client from the cold
- Provide Warmth:
- Remove the person’s wet clothes & Cover with warm blankets, including their face, but not their mouth.
- If Conscious, try to give warm beverages or soup, which can help to increase body temperature
- Apply Hot Applications:
- Apply warm, dry compresses with hot water bottle or warm sponging. Only apply the compresses to the chest, neck, or groin.
- Don’t apply compresses to the arms or legs.
- Applying a compress to these areas will push cold blood back toward the heart, lungs, and brain, which could be fatal.
- Temperatures that are too hot can burn the skin or cause cardiac arrest.
- Volume Resuscitation:
- IV fluids should be administered for patients that have been hypothermic for more than 45-60 mins & to treat Hypotension
EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT
- Endotracheal Intubation: Patients with respiratory failure endotracheal intubation is done and placed on a mechanical ventilator. Intubation and insertion of vascular catheters should not be delayed but performed gently while closely monitoring cardiac rhythm for ventricular fibrillation.
- Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR): For a hypothermic patient in cardiac arrest, perform immediate, high-quality CPR. In situations where performing immediate and continuous CPR.
- Defibrillation: Connect the automated external defibrillator (AED) device electrodes and deliver shock as advised & attempt defibrillation.
REWARMING METHODS:
- External Exogenous Rewarming: Exogenous (active) rewarming methods provide significant external heat which includes large chemical heat pads, large electric heat pads or blankets, warm water bottles, and charcoal-burning Heat Pac.
- Slow Rewarming: Slow rewarming methods include IV solutions heated to 45°C (17 kcal/h); heated, humidified oxygen by mask (30 kcal/h or 0.7°C/h); warmed blankets (0.9°C/h); and heated, humidified oxygen via endotracheal tube (1.2°C/h).
- Moderate Rewarming: Moderate rewarming methods provide heat at approximately 3°C/h. Methods include warmed gastric lavage (2.8°C/h), intravenous solutions heated to 65°C (2.9°C/h), and peritoneal lavage with 45°C fluid at 4 L/h (70 kcal/h or 3°C/h).
- Rapid Rewarming: Rapid rewarming methods provide heat at levels higher than 100 kcal/h. Methods include thoracic lavage at 500 mL/min (6.1°C/h), cardiopulmonary bypass (400 kcal/h or 18°C/h), ECMO, and AV dialysis (1-4 degrees per hour, and warm-water immersion [1500 kcal/h]).
COMPLICATIONS
- Frost Bite: It is a common complication caused by freezing of the body tissues. The skin becomes very cold & red then numb, hard & pale.
- Chilblains: These are painful inflammation of the small cutaneous blood vessels that occur in response to repeated exposure to cold. It causes red itchy patches, swelling & blisters on hands & feet.
- Gangrene: It refers to death of the body tissue due to massive vasoconstriction causing lack of blood flow. The skin becomes red to black, numbness, painful swelling, skin breakdown and coldness in feet & hands
- Trench Foot: It refers to death of the body tissue due to massive vasoconstriction causing lack of blood flow. The skin becomes red to black, numbness, painful swelling, skin breakdown and coldness in feet & hands
PREVENTION OF HYPOTHERMIA
- Appropriate warm clothing in case of exposure to cold weather
- Cover all body parts, and wear hats, gloves, and scarves during the winter.
- Maintain Regular Active Exercises. Take care when exercising outdoors on cold days by dressing in extra layers to prevent heat loss
- Maintain a regular balanced diet to provide Energy & improve Nutrition
- Avoid drinking alcohol when exposed to cold climates as it may cause vasodilation and disrupts temperature homeostasis
- Keep the body dry. Change immediately any clothing that become wet
- Drink warm liquids in cold climates
- Apply heating pads or hot water bottles to warm the hands & feet especially in winters
- Use blankets or quilt while sleeping to keep the body warm
- Adequate heat in the home should be maintained with warmers & heaters.
THANK YOU



