HOSPITALS
DEFINITION
- A hospital is a health care institution for the diagnosis of disease, providing patient treatment with specialized medical and nursing staff and medical equipment.
- The modern hospital also often serves as a center for Investigation, teaching & Research.
CLASSIFICATION OF HOSPITALS
I. Based On the Functions of Hospital
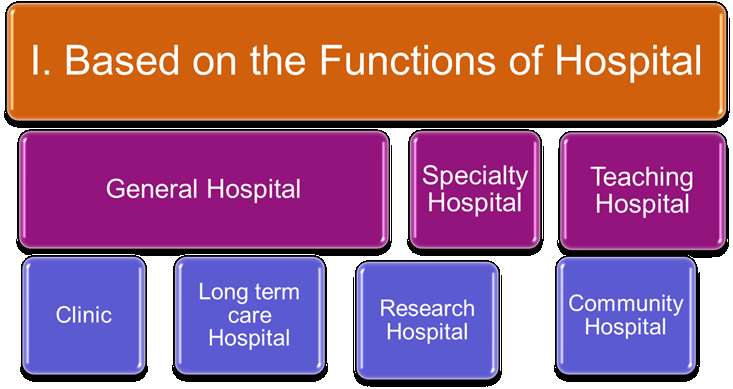
- General Hospitals: They offer little in the way of specialty services and may not be equipped to provide long-term care to patients. Most hospitals today are general service.
- General hospitals focus on general and necessary services for the community, like:
- Surgery
- OB/GYN services
- Pediatric services
- General medical care
- Specialty Hospital: Specialty hospitals treat patients with specific diseases and the physician is specialized in a particular organ systems. Most physicians choose specialization in an area of intense interest or desire and provide treatment for patients with that specific condition.
-Neuro Specialty Hospitals
-Orthopedic
-Ophthalmology
-ENT hospitals etc.
- Teaching Hospitals: A teaching hospital is a hospital that partners with medical and nursing schools, education programs and research centers to improve health care through learning and research. By being at the forefront of medical education and research innovations, teaching hospitals tend to provide many advantages, like:
- Improved quality of care
- New treatments and cures
- State-of-the-art technologies
- Shorter hospitalizations for major illnesses and procedures
- Better outcomes and survival rates
- Specialized surgeries and experimental medical procedures
- The expertise of highly trained physicians and surgeons.
- Clinic: A clinic (or outpatient clinic or ambulatory care center) is a health facility that is primarily focused on the care of outpatients. Clinics can be privately operated or publicly managed and funded. They typically cover the primary care needs of populations in local communities, in contrast to larger hospitals which offer more specialized treatments and admit inpatients for overnight stays.
- Long term care Hospitals: Hospitals providing long-term care can meet the needs of patients suffering from chronic illnesses, requiring psychiatric care, cardiac rehabilitation, or who are going through extensive rehabilitation after accidents or injuries. This might include hospitals that offer burn centers, cancer centers, and similar types of care facilities.
- Research Hospitals: Research hospitals provide care for the most rare and complex conditions, teach future health care providers, and move research results into practice. They work in collaboration and are often collaborated with Faculties of Medicine and other partners. Research hospitals have a significant impact on health, the economy, and the state of knowledge.
- Community Hospitals: Community Hospitals are small local hospitals that provide a range of services to their local community. These can include community beds, maternity, clinics, minor injuries units, X- ray departments etc. Community Hospitals have been part of the health care system for over 150 years and offer a strong tradition of care that local populations have known over generations. These services range from health promotion, diagnostics, treatments, rehabilitation and end of life care.
II. Based on the Size of the Hospital:
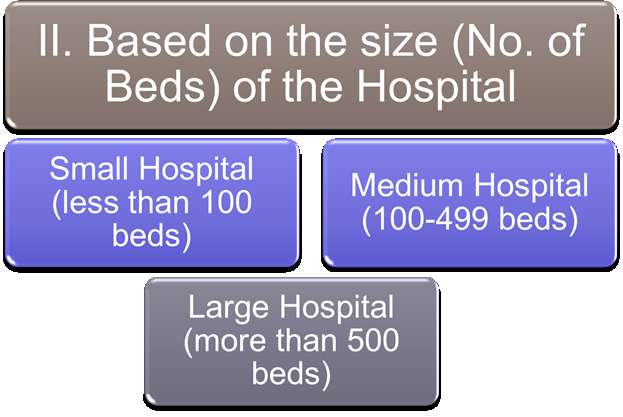
- Small Hospitals: Small Hospitals are licensed with a bed strength of less than 100. Small Hospital deliver services like emergency care, inpatient care, and laboratory testing, but also rehabilitation, long-term care, maternity care, home health care, and even primary care.
- Medium Hospitals: Medium Hospital have a bed strength between 100-300, in some cases they may also exceed to 500 beds. These hospitals provide both traditional & Specialty services.
- Large Hospitals: Large hospitals have bed strength of more than 500. Large hospitals provide services to larger population in the community. These hospitals provide both Acute & long term care and also have specialty units to treat Specific disease conditions. These hospitals also provide opportunities for Education & research
III. Based on Location of the Hospital
- Rural Hospitals: Rural hospitals aid smaller communities and often have limited access to advanced equipment or specialized procedures and techniques.
- Urban Hospitals: Urban hospitals serve larger metropolitan areas and must often offer a wide degree of adaptability when it comes to treatment options and patient experience.
IV. Based on the Ownership
- Private Hospitals: A private hospital is a hospital owned and operated by an organisation other than the state (which may include for-profit and non-profit companies) and which provides care funded other than by the state, for example funded by patients themselves ("self-pay"), by insurers, or by foreign embassies. Private hospitals are commonly part of the majority of healthcare systems around the world.
- Public/ Government Hospitals: A public hospital, or government hospital, is a hospital which is government owned and is fully funded by the government and operates solely without money that is collected from taxpayers to fund healthcare initiatives. In some countries, this type of hospital provides medical care free of charge to patients, covering expenses and wages by government reimbursement.
V. Based on Systems of Medicine
- Allopathic Hospitals: Allopathic medicine is a health system in which medical doctors, nurses, pharmacists, and other healthcare professionals are licensed to practice and treat symptoms and diseases. Treatment is done with medication & Surgery.
- Ayurvedic Hospitals: A medical system from India that has been used for thousands of years. The goal is to cleanse the body and to restore balance to the body, mind, and spirit. It uses diet, herbal medicines, exercise, meditation, breathing, physical therapy, and other methods
- Homeopathic Hospitals: Homeo- Similar, Pathy- Disease Condition. It is formulated based on the so-called PRINCIPLE OF SIMILARITY. According to the homeopathic way of thinking, a disease originates from a disturbance of the patient’s “vital force”. Homoeopathic medicines are used in the form of tinctures, small pills, powders and distilled water. They have the distinct advantage of being free from side effects.
- Unani Systems of Medicine: Unani medicine is a system of alternative medicine that originated in ancient Greece but is now practiced primarily in India. Involving the use of herbal remedies, dietary practices, and alternative therapies, Unani medicine addresses the prevention and treatment of disease.
ORGANIZATION OF HOSPITAL
- Organizational Structure refers to levels of management within a hospital. Levels allow efficient management of hospital departments. The structure helps one understand the hospital's chain of command.
- Hospitals require precision in the execution of job responsibilities and multiple layers of accountability in order to function. To accomplish this, hospitals use a vertical organizational structure with many layers of management.
- Understanding hospital organizational structure ensures that hospital employees know their own responsibilities, the responsibilities of those around them, to whom they report and who to talk to about particular responsibilities or fields of knowledge.
Organizational Structure
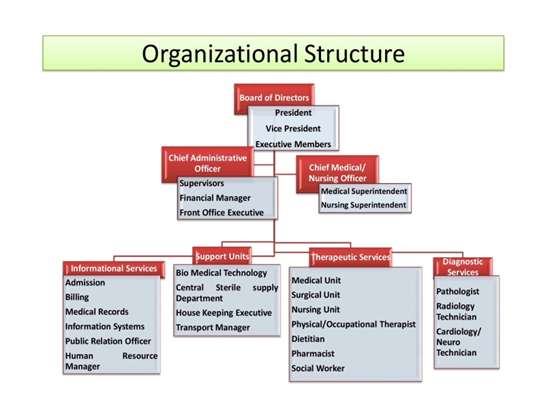
Organization structure
FUNCTIONS OF HOSPITAL
- Hospital administration functions can be classified into five broad categories:
1. Medical function - This involves the treatment and management of patients through health care professionals like Physicians, staff Nurses, technicians etc..
2. Patient Support services - This relates directly to patient care and includes nursing, dietary diagnostic, therapy, pharmacy and laboratory services.
3. Administrative function - which concerns the execution of policies and directions of the hospital governing discharge of support services in the area of finance, housekeeping, laundry, security, transport, engineering and board and the maintenance.
4. Personnel function- Development and administration of a comprehensive manpower development program which includes recruitment and selection, promotion, training, employee welfare and benefits, manpower planning and research.
5. Materials & Supply function- Procurement, storage, inventory, distribution and disposition of hospital supplies, materials, and equipment.




