

IMMUNITY
Definition
Immunity is a state of responsiveness to foreign substances such as micro organisms and tumor proteins. Immune response has three functions.
The body protects against invasions by micro organism and prevents the development of infection by attacking foreign antigens and pathogens
Damaged cellular substances are digested and removed. By this mechanism, the body’s different cell type remains uniform and unchanged.
Mutations abnormality continually crisis in the body but it is normally recognized as foreign cells and destroyed.
TYPES OF IMMUNITY
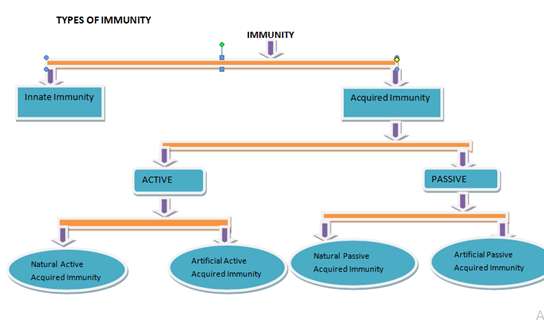
Immunity is classified as innate (natural) or acquired
Lymphoid organs:
The lymphoid system is composed of central and peripheral lymphoid organs
Lymphocytes are produced in the bone marrow and eventually migrate to the peripheral organs. The thymus is important in differentiation and maturation of T-lymphocytes and therefore essential for cell mediated immune response
Lymphocytes:
Lymphocytes are produced in the bone marrow. Lymphocytes differentiate in to Band T lymphocytes.
B-Lymphocytes: B-cells are formed in the bone marrow and differentiate into plasma cells when activated plasma cells produce antibodies (Immunoglobulins)
Cells that migrate from the bone marrow to the thymus differentiate into T-Lymphocytes (Thymus dependent cells). Thymus secretes hormones, (Thymosin) which stimulate the maturation and differentiation of T-lymphocytes. “T” cells are responsible for producing immunity to intracellular viruses, tumor and fungi
T-Lymphocytes can be categorized in to T-Cytotoxic and T-helper cells. All mature T-cells have CD3 antigens
T-Cytotoxic (CD8 or cytolytic cells are involved in attacking antigens on the cell membrane of foreign pathogens and releasing cytolytic substances that destroy the pathogen. Some sensitized ‘T’ cells remain as memory cells.
T-helper (CD4) cells are involved in regulation of cell mediated immunity and the humoral antibody response T cells differentiate into subset of cells that produce distinct types of cytokines. The subsets are called TH1 cells and TH2 cells.
TH1 cell stimulate phagocyte mediated ingestion and killing of microbes, the key component of cell mediated immunity.
TH2 cells stimulate phagocyte dependent, Eosinophils mediated immunity which is effective against parasites and allergic response.
These cells are also responsible in cell mediated immunity. These cells are not T or B cells but are large lymphocytes with numerous granules in the cytoplasm. Natural killer cells are involved in recognition and killing of virus infected cells tumor cells and transplanted cells.
Immune Response
There are two types of immune response in humans namely humoral and cell mediated immunity
|
Characteristics |
Humoral Immunity |
Cell Mediated Immunity |
|
Cells involved |
B-Lymphocytes |
T-Lymphocytes, Macrophages |
|
Products |
Antibodies |
Sensitized ‘T’ cells cytokines |
|
Memory cells |
Present |
Present |
|
Protection |
Bacteria, virus (Extracellular Respiratory and Gastro Intestinal pathogens |
Fungus, Viruses (Intracellular) Chronic infectious agents |
|
Examples |
Anaphylactic Shock. Atopic disease, Transfusion reaction, Bacterial infections |
Fungal infections, Tumor cells, Tuberculosis, contact Dermatitis, graft rejection, destruction of cancer cells |