HUMAN SKELETON
The human skeleton consists of bones and cartilage that form the framework of the body. It includes the endoskeleton and exoskeleton
- Endoskeleton: The endoskeleton makes the major part of the body’s skeletal system and they lie internal to the muscles.
- Exoskeleton: These are vestigial structures that represent the nails, dentin of teeth and bones of the cranial vault.
CLASSIFICATION OF THE ENDOSKELETON
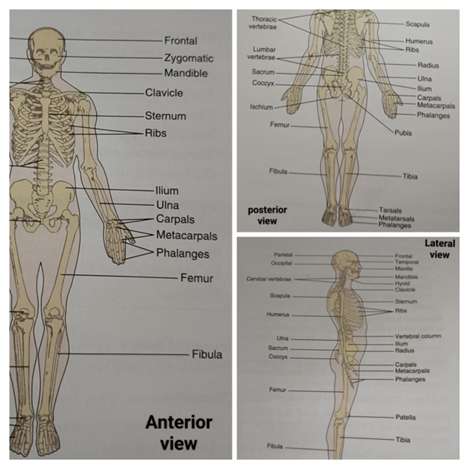
The endoskeleton consists of the facial bones, ribs, clavicles and sternum in the Anterior; and the vertebral Column and Scapulae in the posterior. They are further classified into two(2) as Axial Skeleton and Appendicular Skeleton
- AXIAL SKELETON: This forms the long axis of the body. It consists of skull, hyoid bone, vertebral column, the ribs and the sternum
- Skull: the Skull consists of the cranium and mandible along with the middle ear ossicles
- Cranium: The cranium forms the upper part of the skull and it protects the brain
- Mandible: The mandible is the movable lower part of the skull. The upper part of the facial bones are attached to the cranium and the lower part forms the mandible
- Middle ear Ossicles: There are six (6) bones located in the middle ear (3 in each ear) in the tympanic cavity. They are responsible to transit the sound waves from the tympanic membrane to the inner ear and aid in hearing
- The hyoid Bone: the hyoid bone is located below the lower jaw and is attached by the muscles to the tongue and larynx.
- The Vertebral Column: The vertebral column is also called as backbone or spine that consists of 33 vertebrae that includes 7 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral and 4 coccygeal vertebrae. The vertebral column provides attachments to muscles, supports the trunk, protects the spinal cord and nerve roots and serves as a site for haemopoiesis.
- The ribs: The ribs are the long curved bones and are 24 in number; 12 ribs are present on each side attached to the sternum in the center that forms the thoracic cage and protects the thoracic organs.
- APPENDICULAR SKELETON: It is the portion of the skeleton that supports the appendages. They are 126 in number. It consists of the pectoral girdle or shoulder girdle along with the bones of the upper limb and the pelvic girdle along with the bones of the lower limbs
BONE
Bones are connective tissues that makes up the body’s skeleton and are specialized for providing strength and bearing the weight of the body. There are 206 bones in the human skeleton, not including teeth and sesamoid bones (small bones found within cartilage):
- 80 axial bones. This includes the head, facial, hyoid, auditory, vertebrae, ribs, and sternum.
- 126 appendicular bones. This includes arms, shoulders, wrists, hands, legs, hips, ankles, and feet.
The bone is made up of 3 types of tissue as follows
- Compact Bone Tissue: It is the rigid, harder structure comprising the outer tissue of the bone
- Cancellous Bone Tissue: It is also called as spongy or trabecular bone and is characterized by spongy, porous, honey comb like structure which is usually found at the ends of the long bone
- Sub-chondral Bone Tissue: It is the form of tissue, from which most of the bones develop in children. It is characterized by the smooth tissue at the ends of the bone which is covered by a strong flexible connective tissue called cartilage that is present in adults.
CLASSIFICATION (TYPES) OF BONES
Based on the Size and shape, the bones are classified as follows
- Long Bones: Bones that are longer and wide are called long bones. They are hard, dense bones that provide strength, structure and mobility. Long bones have a long shaft which is primarily a compact bone with two bulky ends that comprises of a large amount of spongy bone tissue.The Long bones contain the yellow bone marrow and red bone marrow which produces blood cells. The Long bones in the upper limbs are the humerus, radius and ulna and the long bones in the lower limbs are femur, tibia and fibula. The clavicles (Collar bone) are also included in the long bones.
- Small Bones: They are smaller in size than the long bones. They differ from the long bones as they have no marrow cavity and have secondary center of ossification at one end. The small bones in the arm are metacarpals and phalanges and in the leg are metatarsals and Phalanges
- Short Bones: Short bones are wide as long bones but they do not have the shaft as in the long bone. It is made up of spongy bone surrounded by compact bone. Short bones also contain the red bone marrow. Typically, short bones facilitate movement and strength in the complex joints of the wrist and ankles. There are 32 short bones that includes
- 16 carpal bones (8) on each arm- these areScaphoid (boat), Lunate(Crescent), Triquetrum(3-cornered), Pisiform(pea), Trapezuim(Table), Trapezoid(quadrilateral), Capitate(head shaped), and Hamate (hook-shaped).
- 14 tarsal bones (7) on each leg- these arecalcaneus, talus, cuboid, navicular, and the medial, middle, and lateral cuneiforms
- 2 knee cap on the right and left leg called the patella bone. Patella is also considered as a sesamoid bone because it primarily provides an anchor point for the tendons and ligaments.
- Flat bones: Flat bones are made up of a layer of spongy bone (with red bone marrow) between two thin layers of compact bone and these bones are the armor of the body. Flat bones provide structure, such as the shape of the head and torso, and framework to the shoulder and hip. Flat bones can also provide protection to the underneath soft tissues.
- Flat bones are the cranial bones, Scapula (Shoulder blade), sternum (breast bone), ribs and iliac bone.
- The bones of the cranium form the skull that encapsulates the brain and are connected together through joints called sutures. Random small bones can develop from the sutured bones along the sutured line called as the sutural bones. The Scapula, sternum, ribs and iliac bone all provide strong points of Insertion for muscles and tendons
- Irregular bones: Irregular bones are made up of cancellous tissue enclosed in a thin layer of compact bone. Irregular bones have a complicated shape with surface markings that are used as point of insertion of muscles, tendons and ligaments is unique for their function.
- Irregular bones are the facial bones (temporal, sphenoid, ethmoid, zygomatic, maxilla, mandible, palatine, inferior nasal concha and hyoid) and bones of the spinal column (the vertebrae, sacrum and coccyx)
- Sesamoid Bone: These are very small bone derived from the Arabic word ‘sesamum’ means small. These bones usually develop randomly in response to excessive strain or friction within a muscle or tendons. Sesamoid bones are located near joint surfaces and embedded on the bony prominences that allows for range of Motion and increased weight bearing activities. Most sesamoid bones are located in the foot, hand, wrist and most well known in the patella.


