REVIEW OF LITERATURE
DEFINITION:
- A literature review is reading surveys books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and that provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated. Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources explored while researching a particular topic and to demonstrates how research fits within a larger field of study.
PURPOSE OF LITERATURE REVIEW
- Place each work in the context of its contribution to understanding the research problem being studied.
- Describe the relationship of each work to the others under consideration.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research.
- Reveal any gaps that exist in the literature.
- Resolve conflicts among seemingly contradictory previous studies.
- Identify areas of prior scholarship to prevent duplication of effort.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature.
TYPES OF LITERATURE REVIEW
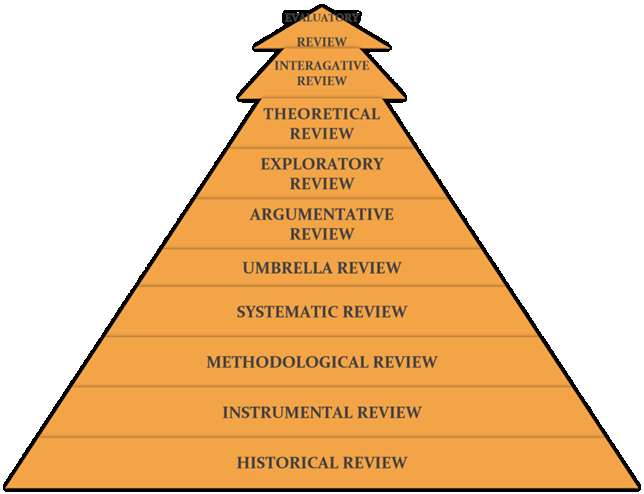
HISTORICAL REVIEW
- Historical literature reviews also called as narrative reviews focusses on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the directions for future research.
INSTRUMENTAL REVIEW
- It is also called as rapid review which critically analyses what is already known about the policy or practice issues and reviewing methods to critically appraise the existing research problem i.e finding out the way to conduct research in a highly specific research issues. It is the state of Identifying how to conduct the research without incurring unnecessary & Unavoidable cost.
METHODOLOGICAL REVIEW
- A review that does not always focus on findings but reviews the method of analysis. Reviewing methods of analysis provides a framework of understanding at different levels like the theory, research approaches, and data collection and analysis techniques, how researchers draw upon a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in all areas of quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection, and data analysis. This approach also highlights the ethical issues that should be considered while conducting the study.
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
- This review consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyze data from the studies that are included in the review. The goal is to deliberately document, critically evaluate, and summarize scientifically all of the research about a clearly defined research problem. Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often on the cause-and-effect relationships. This type of literature review is primarily applied to examining prior research studies in clinical medicine and allied health fields, but it is increasingly being used in the social sciences.
UMBRELLA REVIEW
- It is the review specifically refers to compiling evidence from multiple reviews into one accessible and usable document. It focusses on a broad condition or problem for which there are competing interventions & highlights reviews that determines these Interventions and their results.
ARGUMENTATIVE REVIEW
- This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply imbedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint regarding the nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analysing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of review.
EXPLORATORY REVIEW
- This exploratory review draws on different bodies of literature in order to reformulate the complex challenges of research boundaries between science & wider society by applying newer organizational theory. The purpose in this review is to provide a broad approach to the topic area. i.e The aim is breadth rather than depth and to get a general feel for the size of the topic area.
THEORETICAL REVIEW
- The purpose of this review is to examine the theoretical entity that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. This form of review is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
INTERAGATIVE REVIEW
- This is a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses or research problems. A well-done integrative review must meet the standards of clarity, rigor, and replication. This is the most common form of review in the social sciences.
EVALUATORY REVIEW
- Evaluation Review aims to advance the practice of evaluation and to publish the results of high quality evaluations. The Review focuses on rigorous evaluation of public programs and policies across a range of types of evaluation, policy areas, and academic disciplines, all to foster evidence based policy.


